Vocabulary/Terms:
- Earth – our planet, located on the solar system in the Milky Way galaxy
- culture – way of life, it’s based on location and history and divided into:
- politics (organization of government)
- religion (beliefs)
- economy (interchanging of goods and services)
- Astronomy – study of the universe
- Demography – study of population
- Ecology – study of the environment
- Topography – study of Earth’s physical features
- Oceanography – study of oceans (bodies of water)
- Climatology – study of climates (location)
- Meteorology – study of weather (variations that occur in the atmosphere)
- Geology – study of Earth’s structure and its components (can study fossils and minerals)
- Archeology – study of what people make, build, and do
- Anthropology – study of humans and evolution
- Paleontology – study of dinosaurs
- Geography – study of the Earth
- Absolute Location – an exact location
- Relative Location – a location named using reference points and cardinal directions, a position in relation to other objects
- Hemisphere – a half of the Earth, there are 4 hemispheres: northern, southern, eastern and western
- Equator – latitude that sits at 0°, dividing Earth into northern and southern hemispheres
- Prime Meridian – longitude that sits at 0°, dividing Earth into eastern and western hemispheres
- Latitudes or Parallels – imaginary lines that run to the north and south of the Equator from east to west (horizontally) from 0° to 90° (#° N/S)
- Longitudes or Meridians – imaginary lines that run to the east and west of the Prime Meridian from north to south (vertically) from 0° to 180° (#° E/W)
- Degree – unit of measurement used to identify each latitude & longitude
- Continents – continuous land masses; there are 7: Africa, Antarctica, Asia, Australia, Europe, North America and South America
- Oceans – large bodies of water; there are 4: Pacific Ocean (largest and deepest), Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Ocean and Indian Ocean (smallest)
- Island – a piece of land surrounded by water on all its sides
- Peninsula – a piece of land surrounded by water on 3 sides, but attached to land
- Globe – scale model of planet Earth in sphere form, more accurate than a map, the ideal representation of Earth
- Map – slightly distorted flat representation of the planet
- Cartographer – person who creates maps
- Cartography – art of map making
- Map Projection – ways to transfer a round surface to a flat one
- Topographic or Physical Map – map that represents physical features
- Landsat – satellite belonging to the US which takes images of Earth
- Geographic Information System (GIS) – bank that stores geographical information
- Surveying – process of observing and taking note
- Grid – system of horizontal and vertical lines used to pinpoint any location
- Scale – part of the map that refers to the proportion of the actual distance and the distance on the map, it’s inaccurate because it’s a line and Earth is round
- Great Circle Route – shortest distance between any two points on a map
- Legend or Key – part of the map that defines the symbols and colors used on the map
- Compass Rose – part of the map that displays the four main cardinal points (simple compass rose) and the four subdivisions (complex compass rose)
- Directional Indicator – an arrow pointing either North or South used in certain modern maps instead of the compass rose
- Physical Geography – describes Earth’s topography and physical features
- Political Geography – associated to land borders and people
- Thematic Map – map designed to show a particular theme
- Qualitative Map – map that gives us information directly and briefly, it shows a pattern or tendency and is identified with the use of different colors and shapes
- Flow-Line Map – map that shows movement with the use of arrows
- Cartogram – map that shows information based on geographic features, the map base is distorted to show the information
What is Geography?
- Geography is the study of Earth.
- The word itself is of Greek origin, and means Earth’s description (geo = Earth, graphy = description).
- It’s divided into two parts:
- Physical Geography (topography & location)
- Human Geography (culture)
- Physical geography should always be studied before human geography, since should know where a country is and what it’s like physicalle before learning about its people.
Continents & Oceans

- The seven continents are: North America, South America, Africa, Asia, Australia, Antarctica, and Europe.
- The four oceans are: Pacific Ocean (largest & deepest), Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, and Indian Ocean (smallest)
Globes vs. Maps
- Globes
- Advantages: presents the reality of Earth…
- Disadvantages: no detail, no portability, only one side can be seen at a time…
- Maps
- Advantages: easy to measure location and distance, detailed, portable…
- Disadvantage: distorted…
Qualitative Maps, Flow-Line Maps & Cartograms
- Qualitative Map
- Shows a particular pattern or tendency.
- Situations are repeated.
- Identified with the use of colors/shapes.
- Give us information in a simple and concise form.

- Flow-Line Map
- Shows movement with the use of arrows.
- The thicker the arrow, the larger the quantity; the thinner the arrow, the smaller the quantity.
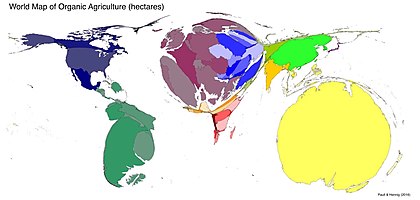
- Cartogram
- Shows information based on geographic features.
- Map base is distorted.
- Larger = more, smaller = less.
The 5 Themes of Geography
- Location (Where is it?)
- Absolute – Latitudes & longitudes or adress (exact)
- Relative – Position referring to other places (reference points)
- Place (What is it like? – singular)
- Physical Geography (topography)
- Human Geography (culture)
- Region (What are they like? – plural)
- Physical Geography (topography)
- Human Geography (culture)
- Movement (constant coming and going)
- people migrate because of economy, politics and religion
- goods are imported and exported through commerce
- ideas are moved through means of communication
- Human-Environment Interaction (relationship between humans and environment)
- Adapt (provide comfort without modifying nature)
- Change (nature is modified)
Map Projections
- Cylindrical Projection (used to make maps of the world)
- i.e. Mercator, Robinson
- Conic Projection (used to make maps of specific places)
- Flat-plane Projection (used to make maps of the poles)
The 5 Parts of a Map
- Title (tells what the map is about)
- Legend/Key (defines the symbols and colors used on the map to help us understand the map)
- Compass Rose (indicates direction, is sometimes substituted for directional indicator)
- Grid (system of imaginary lines that helps us determine absolute location)
- Scale (line on a map that indicates proportional distance on the map)
Key Places on Earth
- The Equator is located on latitude 0°, it divides Earth into northern and southern hemispheres.
- The Prime Meridian is located on longitude 0°, it divides Earth into eastern and western hemispheres.
- Seasons don’t affect Polar Zones nor Tropics very much.
- The Tropics are:
- Tropic of Cancer – 23.5°N
- Tropic of Capricorn – 23.5°S
- The Polar Zones are:
- Arctic Circle – 66.5°N
- Antarctic Circle – 66.5°S
- The Poles are located on:
- North Pole – 90°N
- South Pole – 90°S

No hay comentarios.:
Publicar un comentario